How to memorize faster is a query that has gained more focus as people look for efficient ways to maximize their learning and increase their information retention ability. In a world that continues to evolve new information every second, qualities and capabilities like faster memorization and easy recall skills are a strong asset for anyone. Whether you’re studying for tests, learning a new language, or attempting to recall names at a networking function, effective memory is a game-changer. But is there a magic formula for increasing memory speed? Thankfully, science and experience indicate there is. From evidence-based strategies and methods geared toward speeding up memorization, such as visualization, chunking, spaced repetition, mnemonics, etc., to daily habits such as sleep, diet, and so on, there exist actionable strategies that can improve how fast and how well you memorize. In this blog, we’ll explore proven methods to help you train your brain how to memorize faster and smarter, systematically and sustainably.
By the end of this blog you will find the answers to some of the most commonly asked questions like:
- How to memorize faster and not forget
- How to memorize faster in one day
- How to memorize faster for exams
- How to memorize faster and for a longer time
- How to memorize faster for students
- How to memorize a long answer faster
Memory and Memorization
Two often confusing terms which may seem to have the same meaning but it’s not so. They have completely different meanings. Let’s understand their differences to have a clear idea.
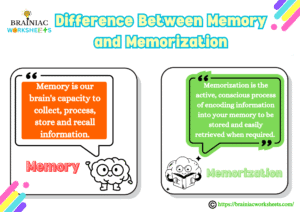
In simple terms, memory is your brain’s capacity to collect, process, store, and recall information. This mechanism enables you to retain experiences, facts, skills, and knowledge so you can use them in the future. It also enables you to recall the past, recognize familiar things, learn new skills, and understand what’s happening around you.
Memory is a complex process where different stages and various regions of the brain work in simultaneous coordination.
You should remember that our brain is not a camera that records every moment with minute details. With time memories can become weak, distorted, and can even disappear. But it’s this amazing ability to learn from the past that makes us what we are and how we understand the world.
Conversely, memorization is the active, conscious process of encoding information into your memory to be stored and easily retrieved when required. It’s the intentional effort you put in to learn and remember certain facts, details, procedures, or skills. As your brain continues to absorb information passively during the whole day, memorization involves applying certain techniques and strategies in order to memorize that information.
In a nutshell, memory is the system as a whole of storing and recalling information, whereas memorization is the conscious series of steps you perform to make that storage and recall more effective and efficient. It’s the step between learning something new and having the ability to recall it when you need to.
Know Your Brain and Understand How It Works
Understanding the way how memory functions is important to know when finding the solution of how to memorize faster. Memory is not a single storage cabinet inside our head; rather, it’s a complex system of various systems that deal with different kinds of information and retain it for varied lengths of time. From the short sensory memories that are temporary for a few seconds to the long-term memories that can linger with us for years, our brain is always processing and storing information. Memory booster techniques are basically strategies that assist us in traversing this complex system, facilitating the process of encoding, storing, and recalling information to be more efficient and effective. Therefore, as we explore further into the realm of faster memorization, remember that we’re not just learning tricks; we’re learning and refining one of the most powerful tools we have – our own memory.
Understanding these fundamental aspects of your brain and how it processes memory empowers you to adopt more effective learning and memorization strategies, ultimately leading to faster and more efficient recall. You’re essentially working with your brain’s natural mechanisms rather than against them.
Misconceptions or Myths about Memorization
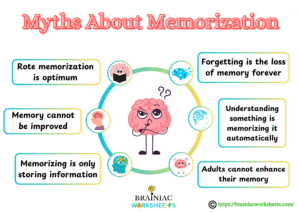
Let’s discuss some common yet widespread misconceptions or myths about memorization:
- Rote memorization is optimum: There is an age-old belief that rote memorization is one of the best memorization methods. Although there is a place for repetition, but continuously repeating and roting layers of information over and over without understanding is ineffective for long time memorization.
- Memory cannot be improved: Memory is not a fixed quality. Like any other skill, it can be developed and mastered with regular practice and the application of effective techniques.
- Memorizing is only storing information: Memorization is not merely overloading facts into your head. It also includes structuring, relating, and understanding the information so that it is easier to recall and apply.
- Forgetting is the loss of memory forever: Forgetting is not always permanent. Memories can be unavailable due to interference or lack of retrieval cues, but they may still exist in the brain and be retrieved under the right conditions.
- Understanding something is memorizing it automatically: Although understanding facilitates memorization, but does not assure it. You must still be actively working with the information and applying techniques to retain it.
- Adults cannot enhance their memory: Although memory may change with age, adults can still improve their memorization abilities by employing the correct methods and practicing mentally stimulating exercises.
By knowing and disproving these myths, you can proceed with memorization with more realistic approach and employ effective methods to increase your capacity to learn and remember faster.
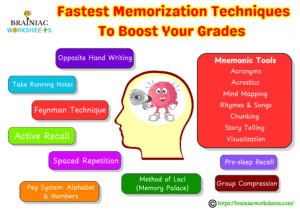
How To Memorize Faster?
In this section you will get to know how to memorize faster using a combined wholesome approach with best memory booster techniques and methods. To effectively become proficient in faster memorization it’s crucial to understand the process, including brain functions, useful techniques, lifestyle aspects, and techniques to overcome everyday challenges. Now let’s discuss in detail how to memorize faster:
Understanding the Basis of Memory
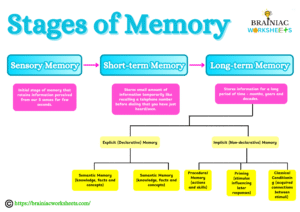
The Stages of Memory
- Sensory Memory: It is the initial stage of memory which briefly retains a huge amount of sensory information (information perceived through our 5 senses) from the surroundings for an extremely brief time (milliseconds to seconds). For example, casually noticing the color of a car that passed by before you focus on something else is your sensory memory in action.
- Short-Term Memory (Working Memory): Temporary storage holding capacity with limited information currently being utilized. Recall of a telephone number long enough to dial it is an example of short-term memory.
- Long-Term Memory (LTM): It stores various types of information for a longer period of time ranging from months, and years to a lifetime. It can be referred to as permanent storage. Types of LTM:
- Explicit (Declarative) Memory: Intentional recollection of facts and events.
Semantic Memory: General knowledge, facts, and concepts.
Episodic Memory: Everyday experiences and events based on time and place. - Implicit (Non-Declarative) Memory: Automatic recall of skills and habits.
Procedural Memory: Knowing how to perform certain actions and skills (motor skills).
Priming: Presenting a stimulus that later influences response.
Classical Conditioning: Acquired connections between stimuli.
The Science of Faster Memorization: Effective Techniques
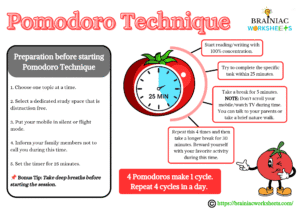
Pomodoro Technique
This is a time management technique invented by Francesco Cirillo. The first step to find the solution of the question of how to memorize faster is to understand how to manage your time while learning and use it effectively. The Pomodoro technique is a study cycle where you study for 25 minutes and take a break of 5 minutes. Repeat this 4 times and then take a 30-minute long break. These 2 hours make one cycle. If you repeat 4 cycles like this daily, you will start observing remarkable improvements. Make sure to choose an undistracted place to study, turn your phone into flight mode, set an alarm for 25 minutes, and tell everyone not to disturb you during this time; you can also use DND boards instead.
Note: Don’t use your mobile phones during the 5-minute breaks, instead, you can take a nature walk or have a conversation with your family.
The “Opposite Hand Writing” Method
Try this unique trick if you want to memorize something instantly. If you are right-handed, write with your left hand and vice versa. When you get out of your comfort zone, your brain has to focus more to get the job done. Attempt writing a math equation 10 times that you believe is difficult to recall using this method. This trick works only to memorize brief information like spellings, formulas, equations, and scientific names; not for long answers. Comment below if it worked for you or not.

Take Running Notes
This turns passive listening into active participation, where your hands are writing down the necessary points. This exercise naturally pulls your attention in the subject because your ears, brain, and hands are all connected and actively participating in this exercise. Always keep in mind, writing down whatever subject you have learned makes the concept clear and helps you to memorize faster.

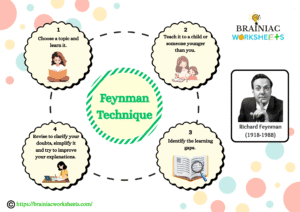
Feynman Technique
This technique was developed by Richard Feynman, who says to try explaining a tricky or complex concept in simple terms to someone younger than you, as if you are teaching it to a child. If you are unable to simplify a concept at this level, identify your learning gaps and repeat the same until you are successful. When you simplify complex ideas, you strengthen your understanding and empower your memory.
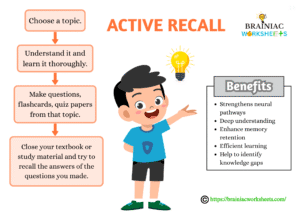
Active Recall
Try recalling information from memory without referring to notes. This strengthens the retrieval track making it smoother and accessible. Through self-testing quizzes, flashcards, and self QnA sessions, you can assess yourself and find out your learning gaps which will encourage you to dive much deeper into the topic. For example, after reading a chapter, try to answer the end-of-chapter questions without looking at the text.
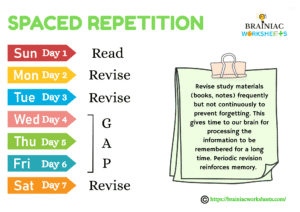
Spaced Repetition
This is also a time management technique like the Pomodoro. Revise study materials (books, notes) frequently but not continuously to prevent forgetting. This gives time to our brain for processing the information to be remembered for a long time. Periodic revision reinforces memory. Employing Spaced Repetition Software (SRS) such as Anki, making your own review schedule, and reviewing notes at increasingly longer intervals (e.g., after 1 hour, 1 day, 3 days, 1 week, etc.). You can also use the 7-3-2-1 spaced repetition study method which means study today (1), revise tomorrow (2), day after tomorrow (3), and on the seventh day (7). Repeat this cycle as required.
Mnemonic Devices
Memory aids that associate new information with more easily remembered information. Following are different types of mnemonic devices used:
Acronyms:
Using the first letter of each word of a list or series to form a new catchy word. For example VIBGYOR for the rainbow colors viz. Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red, PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, Subtraction) in math, HOMES (Huron, Ontario, Michigan, Erie, Superior) for the Great Lakes, FANBOYS (For, And, Nor, But, Or, Yet, So) for coordinating conjunctions. Share more examples that you know in the comment section.
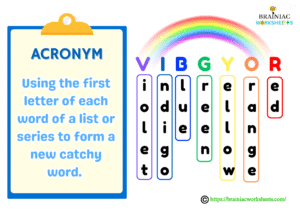
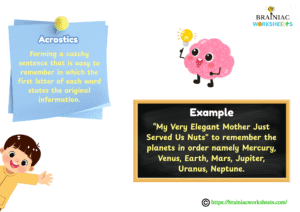
Acrostics (also known as “first-letter mnemonics”):
Forming a catchy sentence that is easy to remember in which the first letter of each word states the original information (e.g., “My Very Elegant Mother Just Served Us Nuts” to remember the planets in order namely Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Uranus, Neptune).
Visualization:
Close your eyes and visualize what you are reading or what is taught in class. Visualization solidifies your abstract idea and convert it into a concrete picture. When a concept appears like a cinema, it’s more likely to be remembered.

Rhymes and Songs:
Arranging the information in a rhythm, song, rhyme or a specific tune before learning makes it easier and faster to remember. This is a powerful trick as it engages our multiple senses creatively. Turn your maths formula into a tune, multiplication tables into a song, or your answer into a rhyme, and see the magic. Many children learn the alphabet and multiplication tables through songs.
How It Works: Music and rhythm is processed deeply by the brain and is highly memorable. Associating information with a melody provides strong retrieval cues. Creates auditory cues that aid recall.

Grouping or Group Compression:
Group the large set of learning materials into identical and smaller categories based on subject, difficulty, visual icons, or any other category. This makes the task manageable and easier for you. Now you can study the grouped materials together without any load.
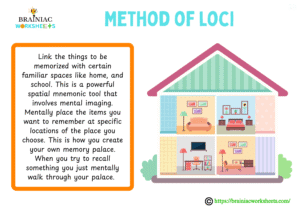
Method of Loci (Memory Palace):
Link the things to be memorized with certain familiar spaces like home, and school. This is a powerful spatial mnemonic tool that involves mental imaging. Mentally place the items you want to remember at specific locations of the place you choose. This is how you create your own memory palace. When you try to recall something you just mentally walk through your palace. For example, imagine walking through your house. In the living room, visualize the signing of the Declaration of Independence. In the bedroom, picture the French Revolution unfolding. In the kitchen, see the Industrial Revolution with gears and steam.
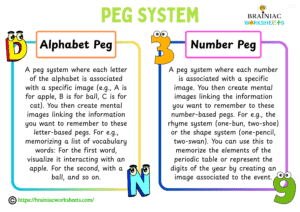
Peg Systems:
There are two types of pegs – alphabet pegs and number pegs.
a. Alphabet Pegs
A peg system where each letter of the alphabet is associated with a specific image (e.g., A is for apple, B is for ball, C is for cat). You then create mental images linking the information you want to remember to these letter-based pegs. For e.g., memorizing a list of vocabulary words: For the first word, visualize it interacting with an apple. For the second, with a ball, and so on.
b. Number Pegs
Similar to alphabet pegs, but each number is associated with a specific image. For e.g., the rhyme system (one-bun, two-shoe) or the shape system (one-pencil, two-swan). You can use this to memorize the elements of the periodic table in order by associating the image of atomic numbers or represent the digits of the year by creating an image associated to the event.
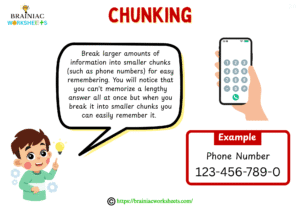
Chunking:
Break larger amounts of information into smaller chunks (such as phone numbers) for easy remembering. You will notice that you can’t memorize a lengthy answer all at once but when you break it into smaller chunks you can easily remember it.
Storytelling:
Create a story that consists of all the components you want to memorize in a logical order. Our brain remembers stories very easily. For example, make a story on seed germination, the water cycle, the Indus Valley civilization, etc. Tell the story to your classmates and friends.

Pre-sleep Recall
Review what you have learned mentally before going to bed. This helps the brain to organize the information you have learned the whole day and transfer it to your subconscious mind from the conscious mind when you are sleeping.
Understanding and Elaborating
- Definition: Thoroughly internalizing the significance of the information and relating it to prior knowledge.
- Mechanism: Produces stronger and more meaningful memory traces, which are easier to retrieve and utilize.
- Real-World Application: Asking “why?” and “how?” questions, paraphrasing information in your own words, explaining it to another person, and identifying real-life examples.
Multi-Sensory Learning: Using more than one sense (visual, auditory, kinesthetic) while learning can produce stronger and more varied memory traces.
- Practical Application: Reading aloud, writing down notes, creating diagrams, using flashcards, role-playing concepts.
- Mind Mapping: Mapping information in a hierarchical format with a central concept and related ideas branching off. Assists in organizing information and viewing connections.
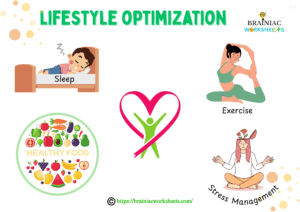
Optimizing Your Lifestyle for Faster Memorization
- Sleep: One of the most powerful tools that most students neglect. An undisturbed sleep of at least 8 hours recharges your brain by strengthening neural connections which helps you to remember and recall timely what you have learned.
- Nutrition: Focus on brain booster foods (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, B vitamins) and drink enough water throughout the day. Avoid eating junk and processed foods.
- Exercise: Regular exercise and meditation increases blood flow and oxygen to the brain, improving cognitive function, including memory.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can decrease memorization power. Do practices like mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and spending time in nature, with friends and family to manage stress levels.
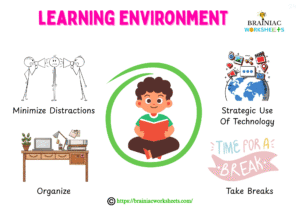
Creating the Ultimate Learning Environment
- Minimize Distractions: Modify your study space into a peaceful space that is free from any distractions (such as noise, frequent interruptions, social media).
- Organize: Keep your study place organized, and well-lit, and make the place comfortable with materials of your choice like small plants, show pieces, or anything that you need to stay focused.
- Strategic Use of Technology: Use offline apps for taking notes, reading PDFs, using flashcards, etc.
- The Power of Breaks: Frequent mini breaks act as supercharging pills that not only declutter your mind but also accelerate memorization.
Use these methods and strategies to improve your memorization and become a better learner.
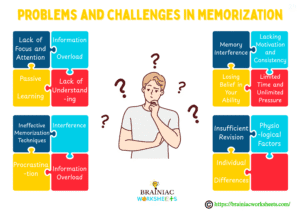
Problems and Challenges in Memorization
Memorization is not easy for everyone. Though there are students who can memorize very easily but it may seem hectic and difficult for many others.
Here are some common problems and challenges encountered in memorization:
- Lack of Focus and Attention: Maintaining consistent focus in a distractive environment is a significant challenge. The information is improperly encoded without proper attention from the beginning of learning which can result in poor recall.
- Information Overload: When the amount of information exceeds the capacity of our brain to process and retain it at a specific time span, it becomes difficult to memorize all at once.
- Passive Learning: Poor memorization is often the result of passive listening or simple reading without active engagement. Inactive learning does not form neural connections which is important for long-term memorization.
- Lack of Understanding: Learning without understanding makes it tough to remember. It’s always easier to memorize and remember when we understand something and then learn it.
- Ineffective Memorization Techniques: Choose the memorization techniques wisely. Solely relying on techniques like rote memorization can provide poor results.
- Interference: Existing memories can sometimes interfere proactively (old information restricting new learning) or retroactively (new information hindering the recall of old information) with the learning and recall of new information.
- Procrastination: Acknowledge your laziness and buckle up.
- Information Overload: Don’t try to memorize too much at a time. Break them into smaller portions and memorize them in specific intervals.
- Memory Interference: You can deal with this issue using the memorization strategies we have discussed further.
- Lacking Motivation and Consistency: A subject that seems boring to you is interesting to others. Ask them the reason for their interest and you will see that you will gradually find reasons to like it. Be consistent with this approach.
- Losing Belief in Your Ability: Never think that you are unable to memorize; make yourself a good memorizer using the memorization strategies that suit you.
- Limited Time and Unlimited Pressure: The extreme pressure to memorize in a limited time causes stress, depression, and anxiety which harms cognitive functions, ultimately disturbing memorization processes.
- Insufficient Revision: Immediately after learning memories don’t get stable automatically. It needs proper revision and practice to memorize and remember it.
- Physiological Factors: Factors like fatigue, stress, poor nutrition, and lack of sleep can greatly damage cognitive functions, including attention, concentration, and memory formation, thus interfering with memorization.
- Individual Differences: Different people learn and understand differently. A one-style-fits-all approach to memorization may prove ineffective for everyone. Identify and use the approaches that work best for you. You will see fruitful results in memorization.
Recognizing and accepting the above challenges moves you a step forward towards memory enhancement. Once you understand the obstacles, you can implement the strategies according to the problems. This will improve memorization providing a fulfilling learning experience.
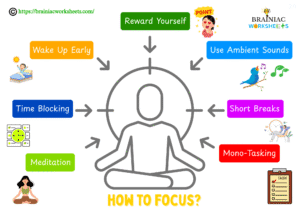
How to Focus?
In this hyper-connected super distractive world maintaining focus and consistent concentration is really challenging but not impossible. Let’s make this difficult task easy and simple. Follow these steps:
Foundation: Setting the Stage for Focus
- Identify Your Peak Focus Times: Notice and mark down the times when you naturally feel focused. Solve the most difficult tasks during that time. Don’t solve difficult tasks when you feel low.
- Create a Dedicated Focus Zone: Dedicate a specific study zone for yourself where you feel focused and undistracted. Spaces like this help your brain to associate neural connections. Always keep the place tidy and well-organized.
- Minimize Digital Distractions: Turn off all notifications on your phone and all other digital gadgets. You can also use the “Do Not Disturb” features or turn your phone into flight mode for a specific time period.
- Communicate Your Focus Needs: Notify your family, friends, or roommates to not disturb you when you are studying. You can hang a “Do Not Disturb” board on your door or something else like this to provide visual cues.
- Break Down Tasks into Smaller, Manageable Chunks: Never attempt to solve lengthy tasks all at once. Break them into smaller portions which makes it easier to learn and memorize.
Practical Techniques to Enhance Focus
- Wake Up Early: If you are a late riser, try to wake up early and gradually make it your habit. In the morning our brain is fresh and fully charged which helps it to absorb information faster and for a longer time. Follow this routine for a month and you will notice a big change.
- Time Blocking: Schedule specific blocks of time in your day for focused work on particular tasks. Treat these blocks like important appointments.
- Meditation: When you are unable to focus, take slow and deep breaths. This helps to calm your nerves and fill your brain with oxygen which will bring back your concentration.
- Mono-Tasking: Don’t try to be a multi-tasker, be a mono-tasker. Our brain cannot focus simultaneously on multiple tasks at the same time.
- Short Breaks: This is essential to maintain consistent focus a short break helps to strengthen neural connections in the brain. It organizes the information and refreshes the brain.
- Use White Noise or Ambient Sounds: Consistent, non-distracting sounds like white noise, nature sounds, or instrumental music block the distractive sounds and help you feel more focused. Try it and figure out which one is suitable for you.
- Reward Yourself: After a successful period of focused work, reward yourself with a small break. This positive reinforcement can motivate you to maintain consistent focus. Try to avoid social media scrolling as a reward because it will break the chain of focus that you have built.
By experimenting with these tips and tricks, you can discover what works best for your needs and train your brain to become a more focused and productive tool. Learning how to focus is a skill that takes time and consistent effort. Have patience and never forget to celebrate your little efforts.
Memory Booster Activities
Now, let us know some memory booster activities that you can use to boost your memory:
1. Engaging Multiple Senses
- Reading Aloud: Combining audio-visual senses.
- Writing and Note-Taking: Kinesthetic involvement helps to encode.
- Drawing Diagrams: Visual representation enhances understanding and recall.
- Using Real Objects: Using real objects to represent concepts solidifies memory.
2. Cognitive Training
- Brain Booster Worksheets: These worksheets rapidly promote cognitive development by stimulating the brain through fun and engaging activities.
Download FREE Brain Booster Resources here 👇🏻
- Puzzles and Games: Activities like crossword puzzles, Sudoku, word search, and memory games can challenge your brain and enhance its cognitive ability. Playing indoor games like chess can also boost your IQ.
- Learning New Skills: Exploring and learning activities like learning a musical instrument or a new language can boost cognitive function.
3. Mindfulness and Meditation
Practice meditation minimum for an hour daily. Start doing smaller sessions initially (5 mins, 10 mins) and then increase the timing. Meditation helps to improve mindfulness (practice focusing but also being aware of the surroundings). This improves the functionality of our working memory. The best time to meditate is in the morning when your mind is naturally calm and fresh.
4. Physical Activity
- Exercise & Workouts: Yoga, walking, dancing, skipping, aerobics, jogging, cycling, and swimming freshen up the mood and improve sleep which reduces stress, depression, anxiety, etc.
- Outdoor Games: Increases the blood flow and oxygen flow into the brain which energizes and forms new blood cells. This process forms strong neural connections.
5. Olfactory Stimulation (Smell Training)
Actively engaging your sense of smell while learning and then re-exposing yourself to the same scent during recall might strengthen memory traces. Specific scents might act as a powerful cue for you to remember or recall something.
6. The “Say It Backwards” Technique
Trying to recall and say it backward can strengthen the auditory memory trace and force a different kind of processing. This unusual practice can find out the gaps in your memory and reinforce the sequence of information.
7. Using Gestures
Pairing relevant gestures with study materials creates a kinesthetic anchor for memorization. Physical experiences leave long-lasting memory impressions.
The memory booster activities are subjective. Their effectiveness varies from person to person. There are so many options available to you, try them and choose the activity or activities that you feel is best for you.

Create Your Own Memorization Technique
Till now you have understood how our brain functions in memorization, how different memorization techniques can be used to memorize faster, memory booster activities, and so on. So now you can create your own memorization technique based on the information you have got till now. Don’t hesitate to invent your own technique and also test it on yourself and others to check whether it works or not.
Conclusion: Your Journey to Faster Memorization
Finally, you have reached the end of this article, and by now, you are fully aware of how to memorize faster using different tips, tricks, and activities. Only by reading and knowing the methods you won’t succeed. Apply and improvise these techniques, methods, and tips further to improve your memorization. If you follow these techniques properly as instructed, you will surely achieve fruitful results and become a better memorizer. Remember, improvement is endless. Have patience, and give time to yourself, you will see that the result is gradually improving. Master the memorization techniques and make them your habit to boost your grades. Continue to experiment, adapt, and refine your approach, and you’ll find that your ability to learn and memorize will accelerate your speed and confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How to memorize faster for exams?
A: Firstly, organize the study materials and use memorization techniques like the Feynman technique, chunking, active recall, and other mnemonic devices. Read this article for more details.
Q: How to memorize faster and for a longer time?
A: Use a combined strategic formula of 3-4 methods like the Pomodoro Technique, spaced repetition, etc. to memorize faster and for a longer time.
Q: What is 3-2-1 rule for study?
A: This rule has many variations, but let me tell you the effective one for memorization:
- Read 3 times.
- Say it 2 times by closing your eyes.
- Write it 1 time without referring to your study material.
Q: What is the 1-3-5-7 rule in studying?
A: It’s a spaced repetition technique where you learn a concept (day 1), revise it after 2 days (day 3), again revise after a gap of two days (day 5), and finally revise it 2 days later (day 7).
Q: What is the 50-50 method of studying?
A: This is a self-testing technique where you use your 50% of the study time in learning, understanding, and memorizing; and use the rest 50% of time explaining the concept without referring to the study material. Try to explain the concept to someone younger than you or you can also explain it to yourself in front of the mirror.
Q: What is the 80-20 method of studying?
A: This is a calculative method, also known as the Pareto Principle, which states focusing 20% on learning can yield 80% result.
I hope this article was helpful.
If you have any query, contact us or comment below.
Thank you,
Simran Mondal.



